LSP2 - ERC725Y JSON Schema
Our JavaScript library erc725.js makes it easy to read + write data encoded according to the LSP2 Schema without manually going through all the encoding complexity.
Introduction
The storage of a smart contract consists of multiple storage slots. These slots are referenced by a slot number (as an integer) starting from slot 0. Each piece of data (= contract state) in a smart contract is stored as raw bytes under a specific storage slot.
In summary, smart contracts understand only two languages: bytes and uint256. Take the following key-value pair, for instance. It is not easy to infer the meaning of these data keys by reading them as bytes.
(key) => (value)
0xdeba1e292f8ba88238e10ab3c7f88bd4be4fac56cad5194b6ecceaf653468af1 => 0x4d7920546f6b656e20322e30
Using slot numbers and raw bytes makes the contract storage very hard to handle. ERC725Y solves part of the problem through a more flexible storage layout, where data is addressed via bytes32 keys. However, with such low-level languages, it is difficult for humans to understand the data in the storage.
The main problem around smart contract storage also arises when data is stored differently, depending on individual use cases and application needs. No standard schema defines "what the data stored under a specific data key represents".
These two issues make it very hard for smart contracts to interact with each other and for external services to interact with contracts' storage.
What does this standard represent?
Specification
The LSP2 Standard aims to offer a better abstraction on top of the storage of a smart contract.
This standard introduces a JSON schema that enables to represent the storage of a smart contract through more understandable data keys. It makes the data stored in a smart contract more organized.

By introducing a schema, we can represent contract storage in the same way across contracts in the network. Everyone has a unified view of the data stored between smart contracts. Developers can quickly parse data, and contracts or interfaces can read or write data from or to the contract storage in the same manner. The standardization makes smart contracts more interoperable with each other.
How does LSP2 work?
LSP2 introduces new ways to encode data, depending on its type. From a single entry to multiple entries (like arrays or maps).
A data key in the contract storage can be defined as a JSON object with properties that describe the key.
{
"name": "LSP4TokenName",
"key": "0xdeba1e292f8ba88238e10ab3c7f88bd4be4fac56cad5194b6ecceaf653468af1",
"keyType": "Singleton",
"valueType": "string",
"valueContent": "String"
}
Data Key Types
A Data Key Type defines HOW a 32 bytes data key is constructed, representing how a particular data key type is described in 32 bytes. For example, Singleton data keys are simple keccak256 hashes of the key name string. Other Data Key Types are constructed of slices of hashes to group different key name parts or define array element keys.
The LSP2 Standard defines several data key types:
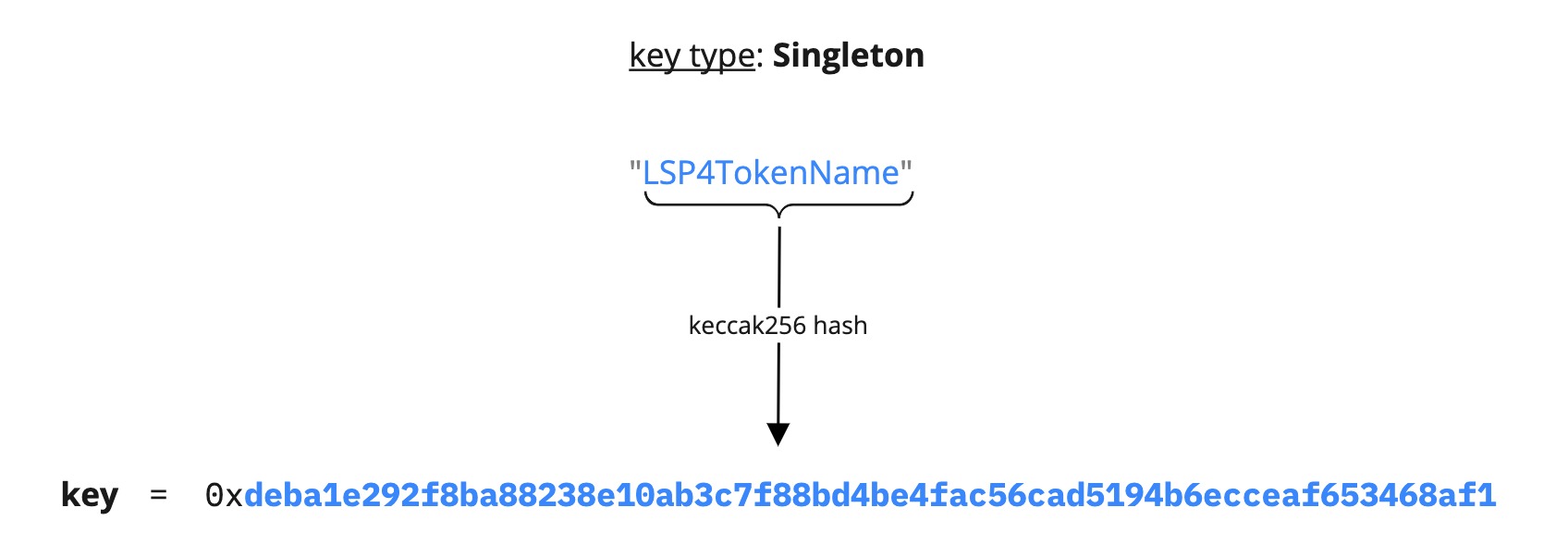
Singleton
A Singleton data key is helpful to store a unique single value under a single data key.
Below is an example of a Singleton data key.
{
"name": "LSP4TokenName",
"key": "0xdeba1e292f8ba88238e10ab3c7f88bd4be4fac56cad5194b6ecceaf653468af1",
"keyType": "Singleton",
"valueType": "string",
"valueContent": "String"
}
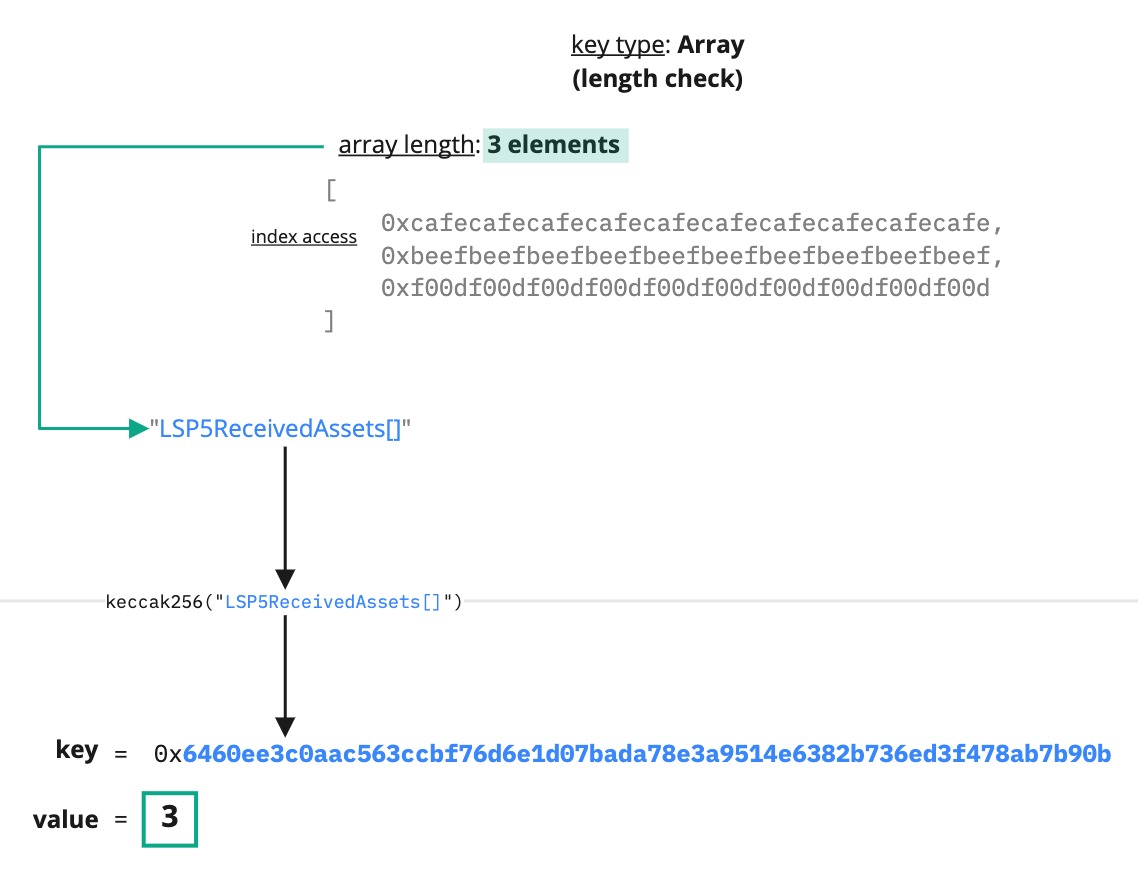
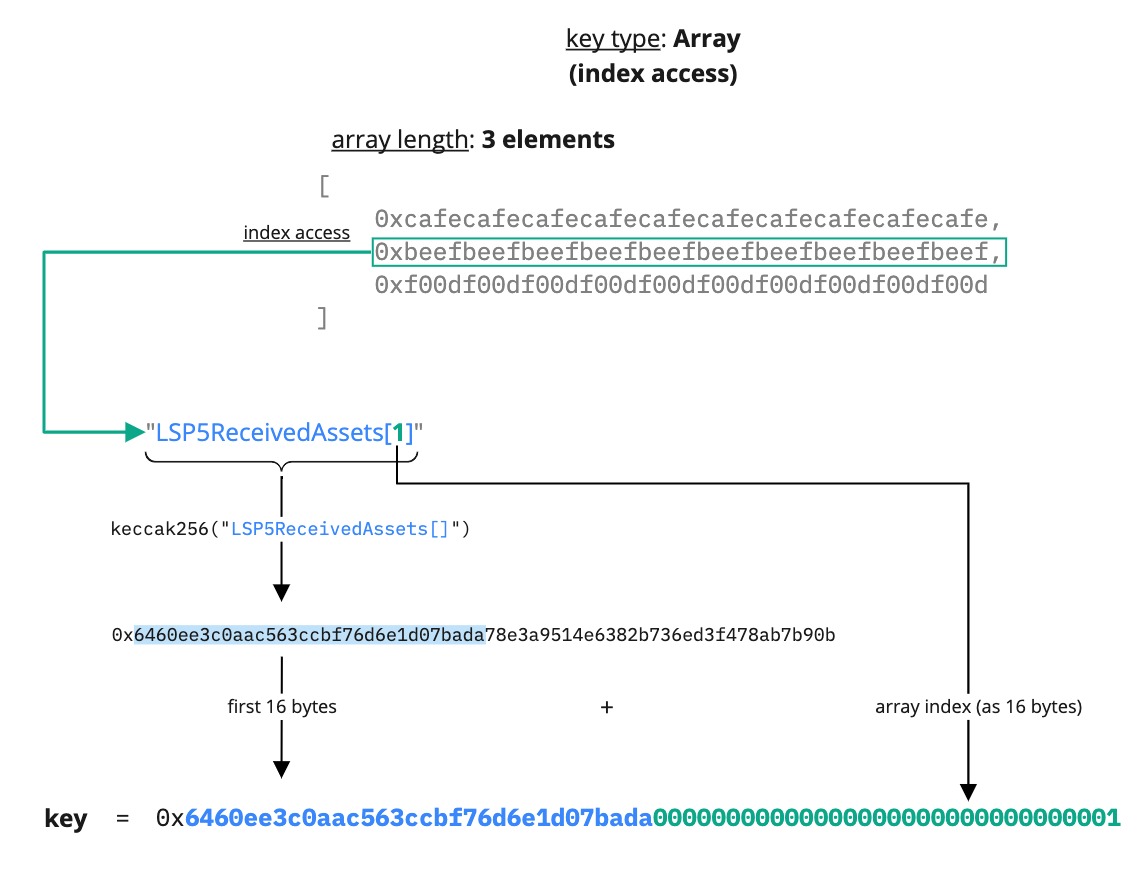
Array
Developers can use a data key of the type Array to store a list of elements of the same data type. They are accessed by an index that defines their position within it.
The Array elements are arranged systematically, in the order they are added or removed to or from it.
The main properties of the LSP2 Array data key type are:
- ordering matters ❗
- duplicates are permitted ✅
A data key type Array can be useful when there is the need to store a large group of similar data items under the same data key. For instance, a list of tokens or NFTs that an address has received. Below is an example of an Array data key:
{
"name": "LSP5ReceivedAssets[]",
"key": "0x6460ee3c0aac563ccbf76d6e1d07bada78e3a9514e6382b736ed3f478ab7b90b",
"keyType": "Array",
"valueType": "address",
"valueContent": "Address"
}
Mapping
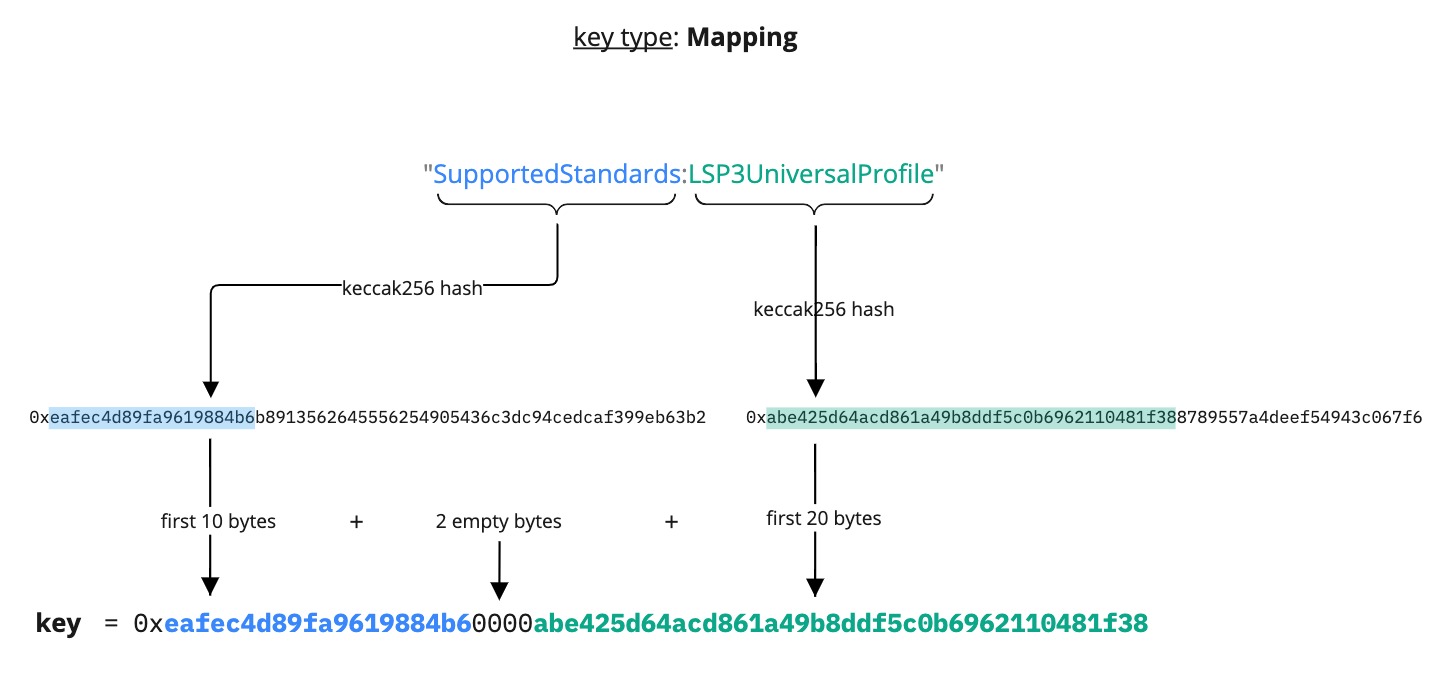
The Mapping data key type is similar to the concept of lookup tables. It can be used to map data that have a shared significance (such as items derived from a common ancestor), and search or query specific elements efficiently.
The main properties of the LSP2 Mapping data key type are:
- ordering does not matter ✅
- duplicates are not permitted ❌
The data being mapped can be words that have a specific meaning for the protocol or application implementation, or underlying data types (= <mixed type>) like address, bytesN, uintN, etc. For <mixed type>, all the data types are left padded. If the type is larger than 20 bytes, the second part of the key is:
- left-cut for
uint<M>,int<M>andbool - right cut for
bytes<M>andaddress
Below are some examples of the Mapping key type.
- mapping to words:
SupportedStandards:LSP3Profile,SupportedStandards:LSP4DigitalAsset,SupportedStandards:LSP{N}{StandardName}, etc... - mapping to
<mixed type>, like anaddress:LSP5ReceivedAssetsMap:<address> - mapping to
<mixed type>, like abytes32:LSP8MetadataAddress:<bytes32>
Example 1: Mapping as FirstWord:SecondWord
{
"name": "SupportedStandards:LSP3Profile",
"key": "0xeafec4d89fa9619884b600005ef83ad9559033e6e941db7d7c495acdce616347",
"keyType": "Mapping",
"valueType": "bytes4",
"valueContent": "0xabe425d6"
}
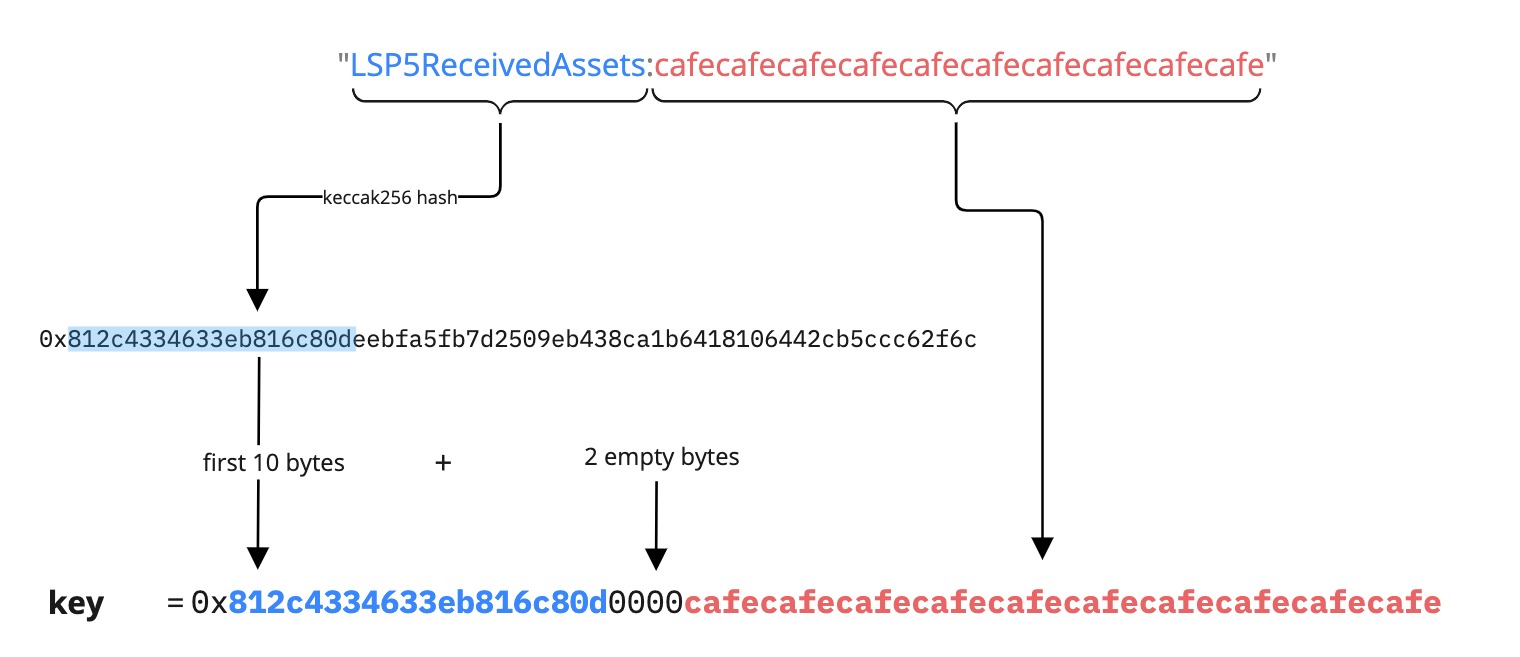
Example 2: Mapping as FirstWord:<address> (<mixed type>)
address value = 0xcafecafecafecafecafecafecafecafecafecafe
{
"name": "LSP5ReceivedAssetsMap:<address>",
"key": "0x812c4334633eb816c80d0000cafecafecafecafecafecafecafecafecafecafe",
"keyType": "Mapping",
"valueType": "(bytes4,uint128)",
"valueContent": "(Bytes4,Number)"
}
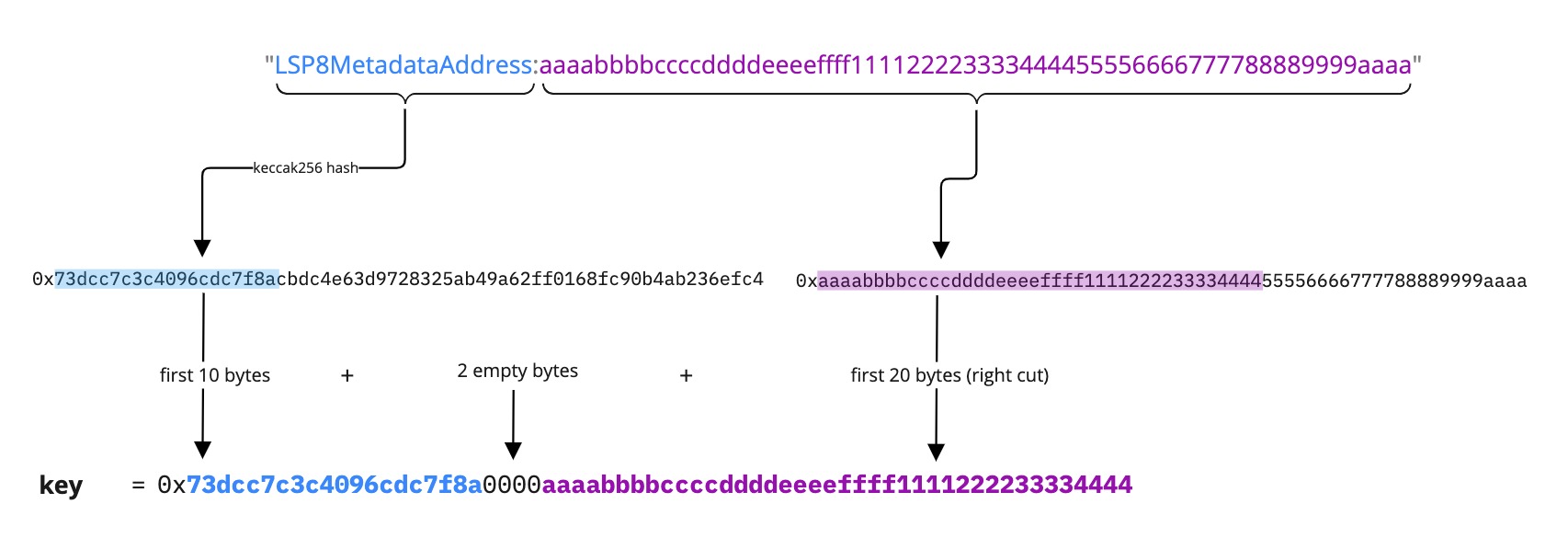
Example 3: Mapping as FirstWord:<bytes32> (<mixed type>)
bytes32 value = 0xaaaabbbbccccddddeeeeffff111122223333444455556666777788889999aaaa.
The bytes32 value is right-cut.
{
"name": "LSP8MetadataAddress:<bytes32>",
"key": "0x73dcc7c3c4096cdc7f8a0000aaaabbbbccccddddeeeeffff1111222233334444",
"keyType": "Mapping",
"valueType": "Mixed",
"valueContent": "Mixed"
}
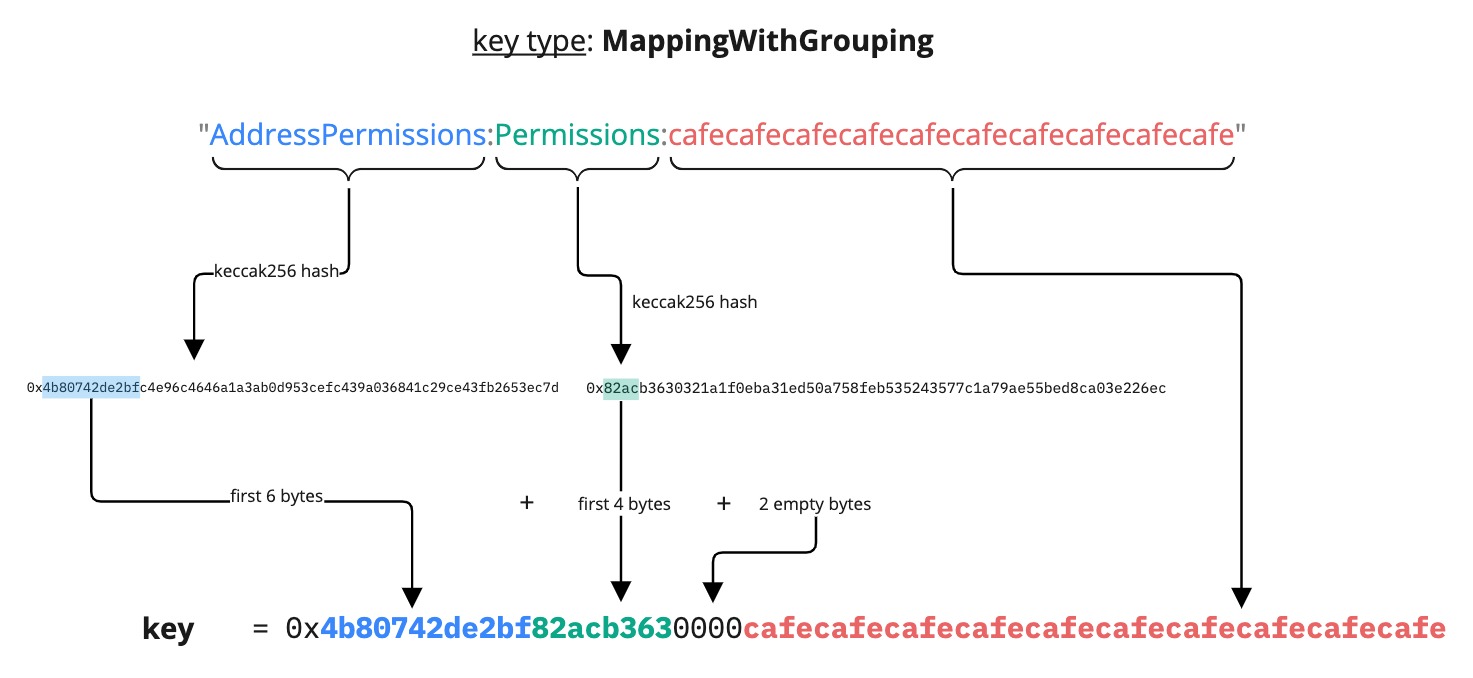
MappingWithGrouping
<firstWordHash>:<secondWordHash>:<bytes2(0)>:<thirdWordHash>
You must take into consideration the fact that if you choose the same value to hash for firstWord and thirdWord there is a 0.0000000233% chance that two random values for the secondWord will result in the same data key.
A data key of type MappingWithGrouping is similar to the Mapping data key type, except that sub-types can be added to the main mapping data key.
For instance, it can be used to differentiate various types from the primary mapping data key, like different types of permissions (see LSP6 - Key Manager).
Below is an example of a MappingWithGrouping data key:
{
"name": "AddressPermissions:Permissions:<address>",
"key": "0x4b80742de2bf82acb3630000<address>",
"keyType": "MappingWithGrouping",
"valueType": "bytes32",
"valueContent": "BitArray"
},
Solidity Example
Whenever you want to generate a data key of keyType MappingWithGrouping:
bytes32 dataKey = bytes32(
bytes.concat(
bytes6(keccak256(bytes(firstWord))),
bytes4(keccak256(bytes(secondWord))),
bytes2(0),
bytes20(keccak256(bytes(thirdWord)))
)
);
valueType encoding
Watch our following video for an overview of how static types (uintM, bytesN, bool), bytes and string are encoded in the ERC725Y storage of a smart contract using the LSP2 standard.
LSP2 differs in terms of how data is encoded depending on its type. As a basic summary, LSP2 and the ABI encoding specification can be compared as follow:
Differences:
- static types (types that have a fixed size like
uintM,bytesNandbool) are encoded as they are without any padding to make a 32 bytes long word. bytesandstringare also encoded as they are as arbitrary bytes, without any 32 bytes words for the offset or the data length.
Similarities
- any array types (e.g:
uintM[],bytesN[],bool, etc...) in LSP2 are ABI encoded the same way as the ABI specification.
Below is a table that describe the LSP2 encoding format for valueTypes.
valueType | Encoding | Example |
|---|---|---|
bool | 0x01 (for true) or 0x00 (for false) | |
string | as utf8 hex bytes without padding ❌ | "Hello" --> 0x48656c6c6f |
address | as a 20 bytes long address | 0x388C818CA8B9251b393131C08a736A67ccB19297 |
uin256 | as a hex value 32 bytes long left padded with zeros to fill 32 bytes | number 5 --> 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005 |
uintM (where N is a multiple of 8 bits in the range8 > N > 256) | as a hex value M bits long left padded with zeros to fill M bytes | number 5 as uint32 --> 0x00000005 |
bytes32 | as a hex value 32 bytes long right padded to fill 32 bytes | 0xca5ebeeff00dca11ab1efe6701df563bc1add009076ded6bcf4c6f771f2e3436 |
bytes4 | as a hex value 4 bytes long right padded to fill 4 bytes | 0xcafecafe |
bytesN (from 1 to 32) | as a hex value N bytes long right padded to fill N bytes | |
bytes | as hex bytes of any length without padding ❌ | 0xcafecafecafecafecafecafecafecafe... |