Adding Custom Data
Universal Profiles are powered by LSP2, a standard that allows them to function as generic key-value data stores. Beyond the predefined data keys from standards like LSP3 Profile Metadata, you can define and set your own completely custom data keys.

This is incredibly powerful for dApps, allowing them to store application-specific information directly on a user's profile without needing a centralized database. For instance, a Web3 e-commerce dApp could store a user's preferred apparel sizes, or a gaming dApp could store a player's settings.
This guide will walk you through defining a custom data key, creating its associated data, and storing it on a Universal Profile. We will use the example of creating an ApparelSize key to store a JSON object with a user's clothing sizes.
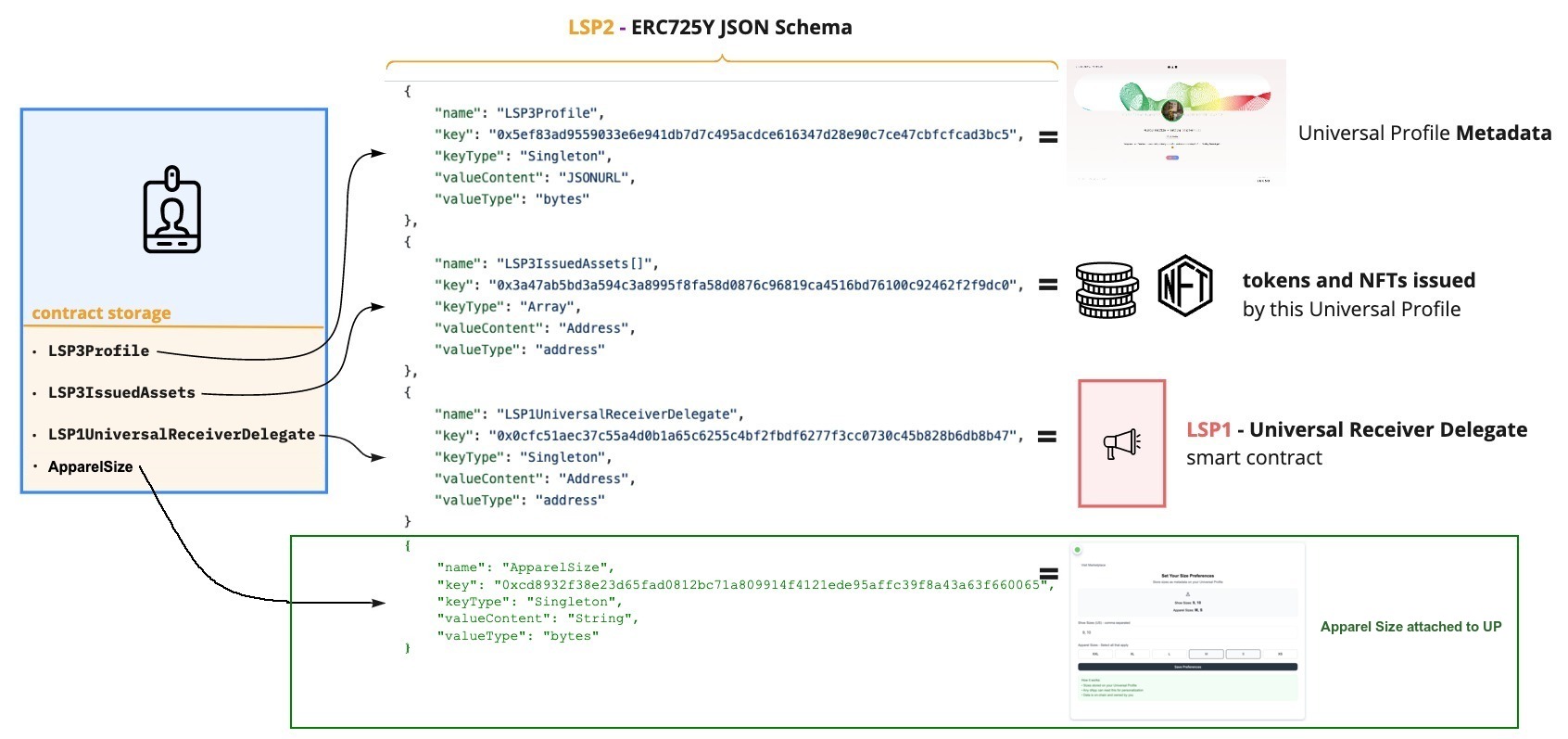
Please check out LSP2 - ERC725Y JSON Schema to see which properties fits best to your needs.
Goal
By the end of this guide, you will be able to:
- Define a custom ERC725Y JSON schema for your new data key.
- Create a JSON file with your custom data and upload it to IPFS.
- Encode the data according to your custom schema.
- Set the custom data on your Universal Profile by sending a transaction.
Prerequisites
- You have a Universal Profile address and and exported the private key of your Browser Extension which has permission to modify the profile's data.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
We'll use erc725.js to handle schema encoding and a web3 library to interact with the blockchain.
- viem
- web3.js
npm install viem @erc725/erc725.js @lukso/lsp-smart-contracts
npm install web3 @erc725/erc725.js @lukso/lsp-smart-contracts
Step 2: Define a Custom Schema
The first step is to define your custom data key. According to the LSP2 ERC725YJSONSchema standard, schemas define the name, bytes32 key, and value format for a piece of data.
Create a file named MyCustomSchema.json. For our example, we'll define a key named ApparelSize. Its bytes32 representation is keccak256('ApparelSize'). We'll specify that its value will contain bytes data (String), which we'll use to store stringified JSON.
{
"name": "ApparelSize",
"key": "0xcd8932f38e23d65fad0812bc71a809914f4121ede95affc39f8a43a63f660065",
"keyType": "Singleton",
"valueContent": "String",
"valueType": "bytes"
}
Step 3: Prepare Your Data
Next, create the JSON object that contains the actual data for your custom key. Since we're storing the data directly on-chain, we don't need to upload it to IPFS.
{
"shoeSize": "US 10",
"shirtSize": "M",
"jacketSize": "L"
}
This JSON object will be stringified, encoded as a string, and stored directly in your Universal Profile's ERC725Y storage.
Since the data saved to blockchain is public and permanent, please avoid storing sensitive information.
Step 4: Encode and Set the Custom Data
Now, we'll write a script to put all the pieces together. It will:
- Load your custom schema.
- Define your JSON data object.
- Stringify the JSON object and encode it as a string for the
ApparelSizedata key. - Send a transaction to your Universal Profile to store the data.
Create a file named set-custom-data.js:
- viem
- web3.js
const {
createWalletClient,
createPublicClient,
http,
getContract,
encodeFunctionData,
} = require('viem');
const { luksoTestnet } = require('viem/chains');
const { privateKeyToAccount } = require('viem/accounts');
const { ERC725 } = require('@erc725/erc725.js');
const MyCustomSchema = require('./MyCustomSchema.json');
const UniversalProfile = require('@lukso/lsp-smart-contracts/artifacts/UniversalProfile.json');
const KeyManager = require('@lukso/lsp-smart-contracts/artifacts/LSP6KeyManager.json');
// --- Configuration ---
const PRIVATE_KEY = '0x...'; // Your EOA private key with permissions
const UP_ADDRESS = '0x...'; // Your Universal Profile address
// ---------------------
const account = privateKeyToAccount(PRIVATE_KEY);
const publicClient = createPublicClient({
chain: luksoTestnet,
transport: http('https://rpc.testnet.lukso.network'),
});
const walletClient = createWalletClient({
account,
chain: luksoTestnet,
transport: http('https://rpc.testnet.lukso.network'),
});
async function setCustomData() {
// 1. Get the UP contract and Key Manager address
const upContract = getContract({
address: UP_ADDRESS,
abi: UniversalProfile.abi,
client: publicClient,
});
const keyManagerAddress = await upContract.read.owner();
const keyManagerContract = getContract({
address: keyManagerAddress,
abi: KeyManager.abi,
client: walletClient,
});
// 2. Define the JSON data to store
const apparelData = {
shoeSize: 'US 10',
shirtSize: 'M',
jacketSize: 'L',
};
// 3. Encode the custom data using your schema
const erc725 = new ERC725([MyCustomSchema]);
const encodedData = erc725.encodeData([
{
keyName: 'ApparelSize',
value: JSON.stringify(apparelData), // Pass the JSON string directly
},
]);
const key = encodedData.keys[0];
const value = encodedData.values[0];
// 4. Encode the `setData` call to be executed on the UP
const setDataCalldata = encodeFunctionData({
abi: UniversalProfile.abi,
functionName: 'setData',
args: [key, value],
});
// 5. Execute via the Key Manager
console.log('Setting custom data on Universal Profile...');
const txHash = await keyManagerContract.write.execute([setDataCalldata], {
gas: 300_000n,
});
console.log('Transaction hash:', txHash);
console.log(
`Custom data set for profile: https://wallet.universalprofile.cloud/${UP_ADDRESS}`,
);
}
setCustomData().catch(console.error);
const { Web3 } = require('web3');
const { ERC725 } = require('@erc725/erc725.js');
const MyCustomSchema = require('./MyCustomSchema.json');
const UniversalProfile = require('@lukso/lsp-smart-contracts/artifacts/UniversalProfile.json');
const KeyManager = require('@lukso/lsp-smart-contracts/artifacts/LSP6KeyManager.json');
// --- Configuration ---
const RPC_ENDPOINT = 'https://rpc.testnet.lukso.network';
const PRIVATE_KEY = '0x...'; // Your EOA private key with permissions
const UP_ADDRESS = '0x...'; // Your Universal Profile address
// ---------------------
const web3 = new Web3(RPC_ENDPOINT);
const myAccount = web3.eth.accounts.privateKeyToAccount(PRIVATE_KEY);
web3.eth.accounts.wallet.add(myAccount);
web3.eth.defaultAccount = myAccount.address;
async function setCustomData() {
// 1. Fetch the UP's Key Manager address
const upContract = new web3.eth.Contract(UniversalProfile.abi, UP_ADDRESS);
const keyManagerAddress = await upContract.methods.owner().call();
const keyManager = new web3.eth.Contract(KeyManager.abi, keyManagerAddress);
// 2. Define the JSON data to store
const apparelData = {
shoeSize: 'US 10',
shirtSize: 'M',
jacketSize: 'L',
};
// 3. Encode the custom data using your schema
const erc725 = new ERC725([MyCustomSchema]);
const encodedData = erc725.encodeData([
{
keyName: 'ApparelSize',
value: JSON.stringify(apparelData), // Stringify the JSON object
},
]);
const key = encodedData.keys[0];
const value = encodedData.values[0];
// 4. Construct the `setData` call to be executed on the UP
const setDataPayload = upContract.methods.setData(key, value).encodeABI();
// 5. Execute via the Key Manager
console.log('Setting custom data on Universal Profile...');
const receipt = await keyManager.methods.execute(setDataPayload).send({
from: myAccount.address,
gas: 300_000,
});
console.log('Transaction successful! Receipt:', receipt);
console.log(
`Custom data set for profile: https://wallet.universalprofile.cloud/${UP_ADDRESS}`,
);
}
setCustomData().catch(console.error);
Before running, replace the placeholder values for PRIVATE_KEY and UP_ADDRESS.
Note that Viem requires explicit chain definitions. We use luksoTestnet from viem/chains. For mainnet, you would use lukso instead.
Then, run the script:
node set-custom-data.js
Step 5: Verify the Custom Data
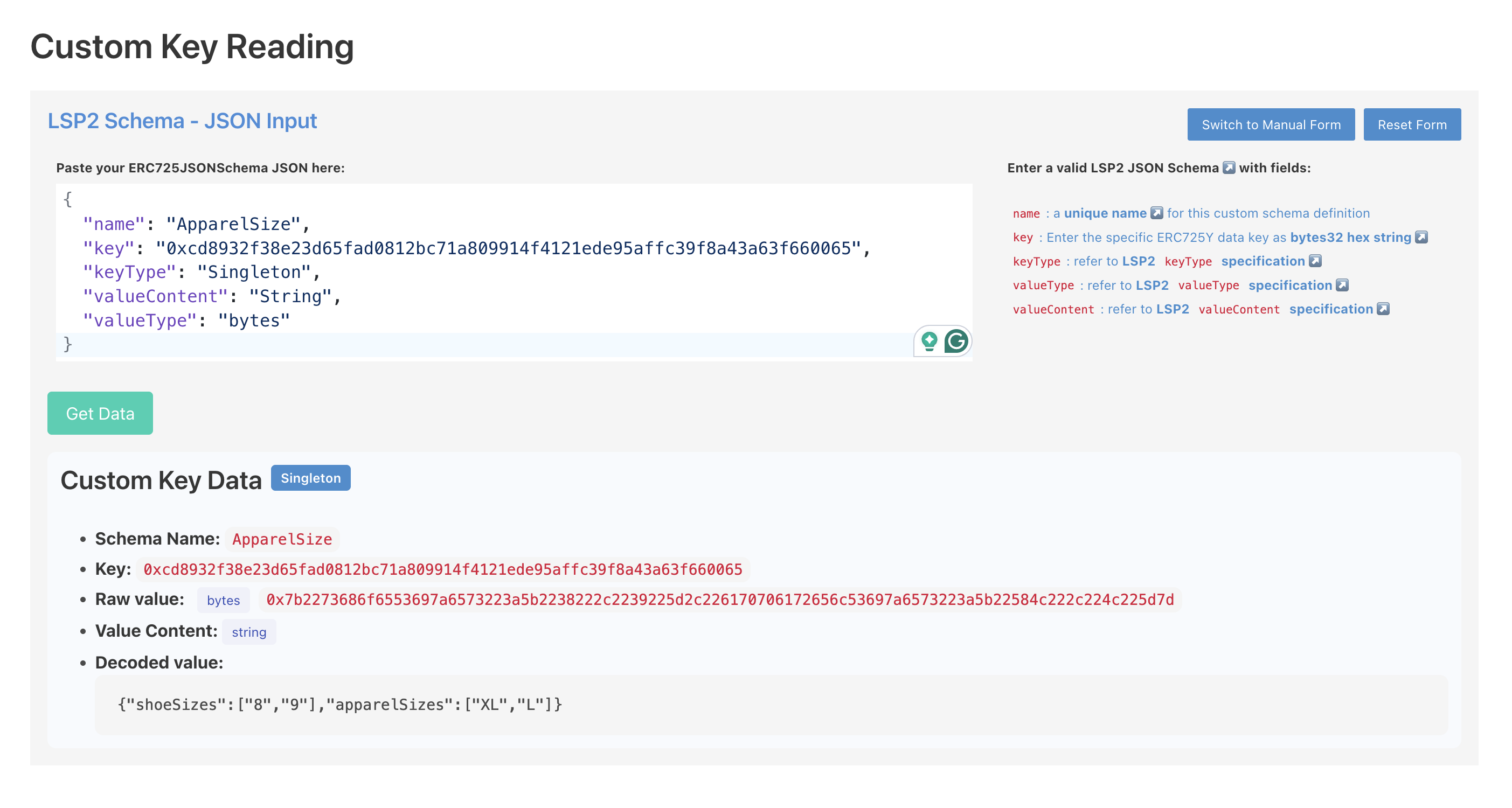
You can use the ERC725 Inspect tool to easily retrieve the custom metadata set on your 🆙:
- Go to the 🔍 inspector page.
- Paste your Universal Profile address in the search field
- Paste the custom schema we defined in MyCustomSchema.json (or the custom schema you created) in the Custom Key Reading section.
- Click the Get Data button
The tool will retrieve the decoded data for you according to the custom schema!
You can also verify that your custom data has been set by reading it directly from your Universal Profile. This script requires your custom schema to decode the on-chain data correctly.
Create get-custom-data.js:
- viem
- web3.js
const { createPublicClient, http } = require('viem');
const { luksoTestnet } = require('viem/chains');
const { ERC725 } = require('@erc725/erc725.js');
const MyCustomSchema = require('./MyCustomSchema.json');
const UP_ADDRESS = '0x...'; // Your Universal Profile address
const publicClient = createPublicClient({
chain: luksoTestnet,
transport: http('https://rpc.testnet.lukso.network'),
});
const erc725 = new ERC725([MyCustomSchema], UP_ADDRESS, publicClient, {});
async function getCustomData() {
const customData = await erc725.getData('ApparelSize');
console.log('Custom "ApparelSize" data:', customData.value);
// Parse the JSON string back to an object
const parsedData = JSON.parse(customData.value);
console.log('Parsed JSON Content:', parsedData);
}
getCustomData().catch(console.error);
const { ERC725 } = require('@erc725/erc725.js');
const MyCustomSchema = require('./MyCustomSchema.json');
const RPC_ENDPOINT = 'https://rpc.testnet.lukso.network';
const UP_ADDRESS = '0x...'; // Your Universal Profile address
const erc725 = new ERC725([MyCustomSchema], UP_ADDRESS, RPC_ENDPOINT, {});
async function getCustomData() {
const customData = await erc725.getData('ApparelSize');
console.log('Custom "ApparelSize" data:', customData.value);
// Parse the JSON string back to an object
const parsedData = JSON.parse(customData.value);
console.log('Parsed JSON Content:', parsedData);
}
getCustomData().catch(console.error);
Run this script to see the decoded ApparelSize data from your Universal Profile. Since we're storing the data as a string on-chain, erc725.js returns the stringified JSON, which we then parse back to the original object.
Use Cases
Storing custom data on Universal Profiles opens up numerous possibilities for dApps and mini-apps:
- E-commerce: Store customer preferences, sizes, purchase history
- Gaming: Store player stats, achievements, game preferences
- Education: Store certifications, course progress, learning preferences
Your custom data keys can be as simple or complex as needed, and you can define multiple schemas for different types of data within the same Universal Profile. The key is to design your schema thoughtfully and consistently so that your dApp and others can reliably read and interact with the data.